Owners of Urbit identities need safeguards that allow for the use of Urbit without jeopardizing cryptographic ownership of their assets. Toward this end, we created the Urbit Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallet for the storage of identities. The Urbit HD Wallet is not one key-pair, but a system of related key-pairs that each have distinct powers, from setting networking keys for communicating in the Arvo network to transferring ownership of identities.
The Urbit HD Wallet's derivation paths have a hierarchical structure, so that keys with different powers can be physically separated. A "master ticket" can re-derive the entire wallet in case of loss. The encryption and authentication keys that identities ships use to sign messages within the network are also derived from the wallet.
Another HD wallet option you may wish to utilize to store your Urbit are hardware wallets such as Trezor or Ledger. We compare this method to the Urbit HD wallet below.
Urbit HD wallets are composed of the following items, which are each assigned to their own individual Ethereum key-pairs.
Master Ticket
Think of your master ticket like a very high-value password. The master ticket is the secret code from which all of your other keys are derived. Technically, your master ticket is a cryptographic seed. You should never share it with anyone, and store it very securely. This ticket can derive all of your other keys: your ownership key and all of the related proxies.
Ownership Address
An ownership address has all rights over the assets deeded to it. These rights are on-chain actions described and implemented in Ecliptic, Azimuth's suite of governing smart-contracts.
Proxies
Each permanent Urbit ID can designate one or more proxies, which are Ethereum addresses capable of a limited subset of Urbit ID transactions, such as spawning planets or rotating keys. The HD wallet automatically generates additional addresses utilized as proxies according to what is appropriate for your Urbit ID.
HD wallet generation
Your Urbit HD wallet is generated from a @q seed called T, which looks
something like ~sampel-ticket-bucbel-sipnem. This is the string known as your
"Master Ticket" that you input into Bridge to sign in. This is put through a
series of algorithms that ultimately generate your keys and the Ethereum
addresses at which they are stored.
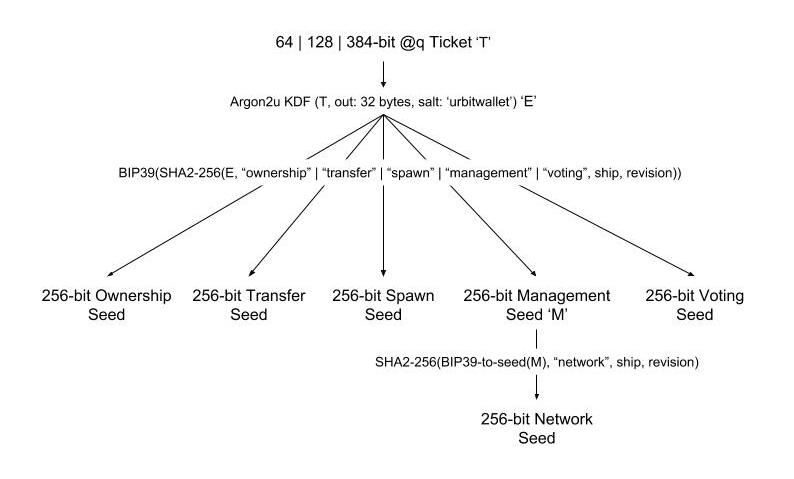
First, your @q is converted into a numeric value E as an intermediary step
by adding salt. Then by
adding additional salts, E is converted into a set of BIP39 seed phrases -
these are 24 word mnemonic sequences used to generate Ethereum wallets. You end
up with one seed phrase for each proxy associated with your ship, and these seed
phrases are then used to generate Ethereum wallets.
One of the wallets will store your Azimuth point, an ERC-721 token, which will be known as your ownership address. Bridge then automatically uses your ownership address to assign the other proxies to the other wallets generated.
ERC-721
Most Ethereum tokens use the ERC-20 standard for smart contracts. Urbit identities are, however, essentially different from most Ethereum tokens, due to identities not being fungible. Since any two stars will handle social-networking realities in a different way, they will carry a different reputation.
The ERC-721 standard, having been made specifically to provide a smart-contract interface for non-fungible assets, serves our needs well. This is the standard that we use for deeding Urbit identities.
Identities, and all of their blockchain operations, are governed by Ecliptic. Ecliptic is an Ethereum smart-contract that governs identity state and the ownership, spawn, management, and voting rights affiliated with your identities.
For the technical implementation details, take a look at Azimuth's Github repository.
Hardware HD wallet
You may also store your Urbit using a hardware HD wallet such as a Trezor or Ledger. This option is used instead of a master ticket - it is a totally separate process from that outlined above. How hardware wallets work are outside of the scope of this document, but here we explain how you may utilize your hardware wallet in a similar fashion to the Urbit HD wallet.
A hardware HD wallet is generated from a seed phrase that should be thought of
as analogous to the @q T used to generate the Urbit HD wallet in the above
diagram. This seed phrase is a human readable sequence of words that may be used
to generate private keys to a near-limitless number of wallets created by adding
salt. Some hardware wallets also allow an additional passphrase to go into the
generation of these wallets. The seed phrase and passphrase should be considered
equal in value to the master ticket T- never share these with anyone!
In order to use your hardware wallet as your Urbit wallet, you first need to generate a set of addresses on which you would like to store your Azimuth point and proxies. Consult your wallet vendor on how to do this. Then login to Bridge using your current method (likely a master ticket) and transfer ownership to the wallet address you generated on your hardware wallet for ownership.
Next, login to Bridge using your hardware wallet. While Bridge supports Trezor and Ledger natively, this may require using Metamask as an intermediary anyways, depending on which firmware you are running. Then accept the transfer. Your Azimuth point is now stored on your hardware wallet.
To finish the process, use Bridge to set your management, voting, and spawn proxies to the other addresses you generated as applicable. You are now using your hardware HD wallet in an analogous fashion to the Urbit HD wallet.
Heightened security practices
A common security pattern is to have "hot" and "cold" wallets. For higher value points such as stars and galaxies, you may consider having your ownership address live on a "cold" wallet that never touches an internet-connected computer, and the various proxies on a "hot" wallet that is permitted to connect to internet-connected devices. This could be accomplished with multiple hardware wallets, a combination of paper and hardware wallet, a hardware cold wallet and Metamask hot wallet, etc. See the User Manual for concrete suggestions on security practices.
One tool useful for this setup is claz, located at app/claz.hoon. claz is
used for making and signing Bridge transactions from an offline computer. A
guide to using claz is available here.